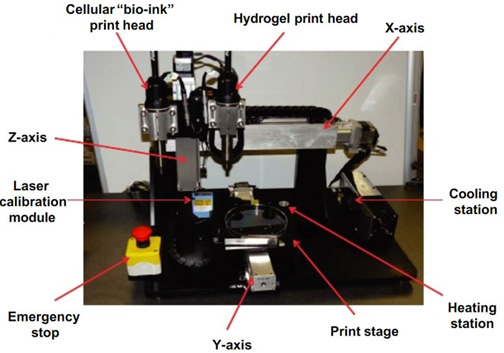
What is aether Industries Ltd?
Be the first! Aether Industries Ltd. engages in the production of intermediates and specialty chemicals. It offers products for pharmaceutical, agrochemical, material science, coating, photography, additive, and oil and gas segments of the chemical industry. The company was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in Surat, India.
What is Proto Labs’ market cap?
Proto labs also recently acquired 3D printing service 3D Hubs for a total $280m, consisting of $130m cash and $150m Proto Labs stock, in what they are calling the biggest ever digital manufacturing deal. 3D printing stock market cap: $2.30b 3D printing share price: $42.53
What is the 3D printing stock market cap?
3D printing stock market cap: To list at $2.1b Formed in 2013 by Greg Mark, Markforged very recently announced a SPAC merger with ONE to list at a $2.1b valuation. Markforged print with composite materials like carbon fiber to produce extremely durable parts, and have moved into metal 3D printing since. This merger is due to close in summer 2021.
How much is bioprinting worth?
The global 3D bioprinting market size was estimated at USD 1.7 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 2.0 billion in 2022....Report AttributeDetailsMarket size value in 2022USD 1.9 billionRevenue forecast in 2030USD 5.3 billionGrowth rateCAGR of 15.8% from 2022 to 2030Base year for estimation202110 more rows
What companies are bioprinting companies?
Bioprinting companies on demand2) CELLINK.3) Aspect Biosystems.5) TeVido Biodevices.6) Digilab.7) Advanced Solutions Life Sciences.8) TRS – Tissue Regeneration Systems.9) nScrypt.12) Nano3D Sciences (n3D)More items...•
Is bioprinting the future?
The global 3-D bioprinting market is projected to grow from $651 million in 2019 to $1.65 billion by 2024, according to a 2019 report by Research and Markets, an Ireland-based firm. As demand for bioprinters and novel biomaterials escalates, the costs of many of these technologies are declining.
Why is bioprinting unethical?
Some of the ethical issues surrounding bioprinting include equal access to treatment, clinical safety complications, and the enhancement of human body (Dodds 2015). 3D printing was invented by Charles Hull in the mid 1980s.
What company is 3D printing organs?
In 2014, a California-based company called Organovo was the first to successfully engineer commercially available 3D-bioprinted human livers and kidneys. 3D printing in healthcare is used to create living human cells or tissues for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering purposes.
What is Bioink made of?
While a wide variety of materials are used for bioinks, the most popular materials include gelatin methacrylol (GelMA), collagen, poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), Pluronic®, alginate, and decellularized extracellular matrix (ECM)-based materials (Table 1).
What is the biggest challenge facing bioprinting?
These are equality, safety and human enhancement.
Who invented bioprinting?
Along with anatomical modeling, those kinds of non-biological uses continue today in the medical field. But it wasn't until 2003 that Thomas Boland created the world's first 3D bioprinter, capable of printing living tissue from a “bioink” of cells, nutrients and other bio-compatible substances.
Has 3D bioprinting been successful?
Additive manufacturing technologies–based 3D bioprinting techniques have made significant progress in recent years for the development of complex geometry. In this process, selection of appropriate bioink, cells, and biomaterials for the effective fabrication of targeted tissue plays crucial role.
Why is 3D bioprinting bad?
The scope of 3D bioprinting includes not only the issues of the advanced technologies of human tissues and organs printing but also raises a whole layer of interdisciplinary problems of modern science, technology, bioethics, and philosophy.
What are the disadvantages of 3D bioprinting?
Disadvantages include lack of precision with regards to droplet size and droplet placement compared to other bioprinting methods. There is also a requirement for low viscosity bioink, which eliminates several effective bioinks from being used with this method.
How will bioprinting be used in the future?
Bioprinting could eventually be the preferred platform to utilize human stem cells to produce artificial solid tissues and organs. The combination of 3D bioprinting with microfluidics allows the development of the next generation of organ-on-a-chip platforms.
When was the first 3D printed organ transplant?
1999. The stroke of the new millennium saw a world first as the first 3D printed organ was transplanted into a human. Created by scientists at Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, a human bladder was printed, covered in the recipient's own cells, and then implanted.
What is 3D Bioprinting used for?
Bioprinting is an extension of traditional 3D printing. Bioprinting can produce living tissue, bone, blood vessels and, potentially, whole organs for use in medical procedures, training and testing.
What is the process of Bioprinting?
Bioprinting is an additive manufacturing process similar to 3D printing – it uses a digital file as a blueprint to print an object layer by layer. But unlike 3D printing, bioprinters print with cells and biomaterials, creating organ-like structures that let living cells multiply.
How does 3D Bioprinting work?
“3D Bioprinting” or “bioprinting” is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and biomaterials instead of traditional metals and plastics to create 3D constructs that are functional 3D tissues. These biomaterials are called bioinks, and they mimic the composition of our tissues.
About Ather Energy Stock
Ather Energy is a manufacturer of electric scooters and electric vehicle charging network called AtherGrid.
Press
EquityZen helps investors to access private companies and their employees to sell shares.